- Home » Blog » Tech Business World » Management Information Systems (MIS) » Overview of Management Information Systems
Overview of Management Information Systems
Management Information Systems (MIS) are computerised systems that collect, process, and distribute information to support organisational decision-making, operations, and strategic planning. They encompass hardware, software, data, procedures, and people, providing timely and relevant information to improve efficiency, decision-making, and competitive advantage.
Date Posted: Fri 14th Jun, 2024
A Management Information System (MIS) is a computerised system that collects, processes, stores, and distributes information to support decision-making, coordination, control, analysis, and visualisation of information within an organisation.
The primary objectives of an MIS are:
To provide accurate, timely, and relevant information to managers and decision-makers. Data provided to those in managerial or decision-making roles is:
- Accurate: The information must be free from errors and reliable. Inaccurate information can lead to poor decisions, so the integrity of data is crucial.
- Timely: The information must be available when needed. Timeliness is essential because outdated information might not reflect the current situation, leading to decisions based on obsolete data.
- Relevant: The information must be pertinent to the specific needs of managers and decision-makers. It should be applicable to the task at hand and support the decision-making process effectively.
To support the planning, control, and operational processes of an organisation.
1. Planning
- Strategic Planning: An MIS provides long-term data analysis to help managers and executives in formulating strategic goals and objectives. This includes forecasting, trend analysis, and scenario planning.
- Tactical Planning: It aids in medium-term planning by providing detailed reports and analytics that help in setting objectives for departments, projects, or teams.
- Operational Planning: On a day-to-day basis, the MIS supports short-term planning by offering real-time data and insights to manage daily activities and immediate needs.
2. Control
- Monitoring Performance: An MIS helps in tracking the performance of various aspects of the organisation against set targets or benchmarks. This includes financial performance, productivity metrics, and operational efficiency.
- Feedback Mechanism: It provides a continuous feedback loop where data from operations is analysed and fed back into the system to adjust processes and improve outcomes.
- Regulatory Compliance: Ensures that the organisation complies with internal policies and external regulations by tracking and reporting relevant data.
3. Operational Processes
- Automation of Routine Tasks: An MIS can automate repetitive tasks, thereby increasing efficiency and reducing the chance of human error. This includes tasks such as data entry, report generation, and inventory management.
- Improved Decision-Making: By providing timely and relevant information, an MIS supports managers in making informed decisions quickly and effectively.
- Resource Management: It helps in optimising the use of resources, including human resources, equipment, and materials, by providing accurate and up-to-date information on resource availability and utilisation.
- Coordination and Communication: Facilitates better communication and coordination among different departments and teams within the organisation by ensuring that everyone has access to the same data and insights.
4. Benefits
- Efficiency: Enhances the efficiency of business processes by streamlining operations and reducing redundancy.
- Productivity: Boosts productivity by providing tools and information that help employees perform their tasks more effectively.
- Agility: Increases organisational agility by enabling quick responses to changes in the market or internal environment through better-informed decisions.
To help managers make better decisions by providing them with the right information at the right time.
Key Aspects:
1. Right Information:
- Relevant Data: MIS ensures that the data provided to managers is relevant to their specific needs and decision-making contexts. This relevance helps in focusing on the key issues without being distracted by extraneous information.
- Accurate Data: The system provides reliable and precise information, minimising errors and reducing the risk of making decisions based on faulty data.
- Comprehensive Reports: MIS can generate detailed reports that give a holistic view of the situation, combining data from various sources to provide a complete picture.
2. Right Time:
- Timeliness: In the fast-paced business environment, having up-to-date information is crucial. MIS ensures that data is current and available when needed, enabling timely decisions.
- Real-Time Data: Many MIS are equipped with real-time data processing capabilities, which allow managers to make decisions based on the latest available data.
Benefits to Decision-Making:
1. Improved Efficiency:
- Speed: Quick access to relevant information reduces the time managers spend on data collection and analysis, allowing faster decision-making.
- Streamlined Processes: Automation of routine data gathering and report generation frees up managers to focus on higher-level strategic thinking.
2. Enhanced Effectiveness:
- Informed Decisions: With accurate and timely information, managers can make well-informed decisions that are more likely to lead to successful outcomes.
- Risk Mitigation: Access to comprehensive data helps in identifying potential risks early and allows for better planning to mitigate these risks.
3. Strategic Planning:
- Forecasting: MIS can help in predicting future trends based on historical data, aiding in strategic planning and long-term decision-making.
- Scenario Analysis: Managers can use MIS to run various scenarios and assess potential outcomes, which helps in making more robust strategic decisions.
4. Operational Control:
- Monitoring: MIS helps in tracking the performance of various processes and operations, ensuring that they are aligned with the organisational goals.
- Feedback Mechanism: Continuous feedback through MIS allows for adjustments and improvements in operations and strategy implementation.
Practical Applications:
- Financial Management: MIS provides detailed financial reports and dashboards that help managers track budgets, expenses, and revenues in real-time.
- Inventory Management: MIS helps in maintaining optimal inventory levels by providing timely data on stock levels, sales trends, and supplier performance.
- Customer Relationship Management (CRM): MIS can integrate with CRM systems to provide insights into customer behaviours and preferences, aiding in better customer service and targeted marketing strategies.
These objectives are critical because they help managers and decision-makers to:
- Make Informed Decisions: With accurate, timely, and relevant information, managers can make well-informed decisions that align with the strategic goals of the organisation.
- Enhance Efficiency: Timely information helps in reducing delays and improving the speed of operations, leading to increased organizational efficiency.
- Improve Problem-Solving: Relevant information allows managers to understand issues better and devise effective solutions.
- Support Strategic Planning: Accurate data is essential for long-term planning and forecasting, which is vital for the sustained growth and success of the organisation.
- Providing a structured and systematic way to collect, process, store, and disseminate information, thereby enhancing the overall efficiency, effectiveness, and agility of the organisation.
- Provide the right information at the right time thereby empowering managers to make decisions that are not only timely but also informed and effective. By ensuring that the data is relevant, accurate, and timely, MIS enhances the overall decision-making process, leading to improved efficiency, effectiveness, and strategic alignment within the organisation.
In essence, an MIS aims to provide a robust framework for collecting, processing, storing, and disseminating information to ensure that the organisation operates efficiently and effectively.
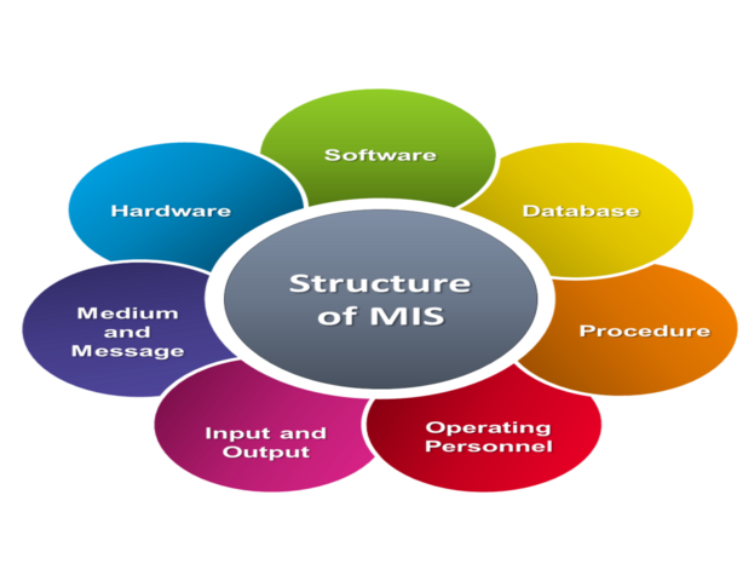
Key Components of an MIS:
- Hardware: This includes the physical computer systems, servers, networking equipment, and other devices used to run the MIS.
- Software: The software component includes system software, application software, and database management systems that facilitate the operations of the MIS.
- Data: MIS relies on various types of data, including transactional data, master data, and metadata, which are organised and stored in databases.
- Procedures: This component includes the rules, policies, and procedures that govern the operation of the MIS, such as data entry procedures, security protocols, and backup processes.
- People: The people component includes end-users, system analysts, programmers, and other personnel who interact with the MIS or manage its operations.
Types of Information Systems within an MIS:
Transaction Processing Systems (TPS):
These systems record and process routine business transactions, such as order processing, inventory management, and payroll. They are a type of information system that collect, store, modify, and retrieve the data transactions of an organisation. Within the broader framework of a Management Information System (MIS), TPS serve as the foundation for business operations, ensuring that daily transactions are processed efficiently and accurately.
Key Characteristics:
- Real-Time Processing: TPS often operate in real-time, processing transactions as they occur. This ensures that the data is always current and accurate, which is crucial for decision-making and operational efficiency.
- High Volume: These systems are designed to handle a high volume of transactions. Examples include sales transactions in retail stores, deposit and withdrawal transactions in banks, and order processing in e-commerce.
- Reliability and Consistency: Reliability is paramount in TPS. They must be robust and resilient, ensuring data integrity and consistency. This is achieved through mechanisms like error-checking and redundancy.
- Automated Data Processing: TPS automate the process of data collection and entry, reducing the likelihood of human error and increasing efficiency.
- Detailed Reports: They generate detailed reports that provide insights into transaction patterns and operational metrics. These reports can be used by management to monitor and optimise business processes.
Functions of TPS:
- Data Collection: TPS collect data from transactions such as sales, receipts, payments, and orders. This data is then used for various operational and analytical purposes.
- Data Storage: Collected data is stored in databases for future retrieval and analysis. The storage systems are designed to ensure data security and accessibility.
- Data Processing: The system processes data to update records and generate outputs like receipts, invoices, and reports. Processing can be batch (where transactions are collected and processed at a scheduled time) or real-time (processed immediately).
- Data Output: TPS provide outputs in various forms such as transaction logs, detailed reports, and summaries which help in operational management and decision-making.
Examples of TPS:
- Point of Sale (POS) Systems: Used in retail to record sales transactions, update inventory, and generate receipts.
- Automated Teller Machines (ATM): In banking, ATMs process transactions like cash withdrawals, deposits, and balance inquiries.
- Order Processing Systems: In e-commerce and logistics, these systems manage order entry, inventory management, and shipment processing.
Impact on Organisations:
- Operational Efficiency: By automating routine transactions, TPS improve the speed and efficiency of business operations, reducing manual effort and errors.
- Data Accuracy: Ensuring that transactional data is accurate and up-to-date aids in maintaining the integrity of financial records and customer information.
- Customer Service: Efficient transaction processing enhances customer experience by reducing wait times and ensuring accurate service delivery.
- Decision Support: Data generated and processed by TPS provides valuable insights for strategic planning and decision-making.
- Scalability: TPS can scale with business growth, handling increasing volumes of transactions without compromising performance.
Integration with MIS: In a comprehensive MIS, TPS integrate with other information systems such as:
- Management Reporting Systems (MRS): They utilise data from TPS to generate periodic reports for management analysis and decision-making.
- Decision Support Systems (DSS): These systems use transactional data to create models and simulations that help in strategic decision-making.
- Executive Information Systems (EIS): EIS provide top executives with easy access to key performance indicators and critical data, often derived from TPS.
Transaction Processing Systems are fundamental to the smooth operation of any organisation. By ensuring accurate and efficient handling of transactions, TPS support the broader objectives of an MIS, enabling better decision-making, operational control, and strategic planning. Their role in collecting, processing, and outputting transactional data makes them indispensable in modern business environments.
Management Information Systems (MIS):
These systems provide reports and summarised information to support managerial decision-making. They are integrated systems that provide managers with the tools to organise, evaluate, and efficiently manage departments within an organisation. They combine software, hardware, procedures, and personnel to provide detailed reports on various aspects of the organisation's operations. MIS is crucial for decision-making and strategic planning within an enterprise.
Key Characteristics:
- Data Integration: MIS integrates data from various sources and departments, ensuring a comprehensive view of the organisation’s operations.
- User-Friendly Interface: It features interfaces that are easy to navigate for managers and decision-makers, providing quick access to critical data and reports.
- Regular Reporting: MIS generates periodic reports that help in tracking performance, monitoring progress, and making informed decisions.
- Support for Decision-Making: The system aids managers in making strategic, tactical, and operational decisions by providing relevant data and analytics.
- Real-Time Data Processing: MIS can process data in real-time, ensuring that managers have the most current information at their disposal.
Functions of MIS:
- Data Collection: MIS collects data from internal and external sources, including transaction processing systems, market research, and competitive intelligence.
- Data Storage: The system stores data in databases, ensuring it is secure, organised, and easily retrievable.
- Data Processing: MIS processes raw data into meaningful information through sorting, aggregating, and summarising.
- Data Output: It produces reports, visual dashboards, and other outputs that help managers understand performance metrics and business trends.
- Decision Support: MIS provides analytical tools and simulations to support decision-making processes.
Types of MIS Reports:
- Scheduled Reports: Generated at regular intervals (daily, weekly, monthly) to monitor routine operations.
- Exception Reports: Highlight significant deviations from the norm, prompting managers to investigate and take corrective actions.
- Demand Reports: Generated on an ad-hoc basis to address specific queries or issues.
- Predictive Reports: Utilise historical data and analytical models to forecast future trends and performance.
Impact on Organisations:
- Enhanced Decision-Making: By providing accurate and timely information, MIS enhances the quality of managerial decisions.
- Increased Efficiency: Automating data collection and reporting processes reduces manual effort and increases operational efficiency.
- Improved Coordination: MIS facilitates better communication and coordination among different departments by integrating data across the organisation.
- Strategic Planning: It supports long-term strategic planning by providing insights into market trends, competitive analysis, and internal performance metrics.
- Operational Control: Managers can monitor daily operations and ensure that they align with organisational goals and standards.
Integration with Other Information Systems:
- Transaction Processing Systems (TPS): TPS feed transactional data into MIS, ensuring that all operational data is up-to-date and accurate.
- Decision Support Systems (DSS): DSS leverage the data from MIS to perform complex analyses and simulations for strategic decision-making.
- Executive Information Systems (EIS): EIS use MIS data to provide top executives with high-level summaries and key performance indicators.
- Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP): ERP systems integrate various business processes and functions, and the data generated by ERP can be used by MIS for reporting and decision-making.
Examples of MIS Applications:
- Sales and Marketing: MIS can track sales performance, analyse market trends, and measure the effectiveness of marketing campaigns.
- Human Resources: It helps in managing employee records, tracking performance, and planning for staffing needs.
- Finance and Accounting: MIS supports budgeting, financial reporting, and analysis of financial performance.
- Operations and Production: It aids in monitoring production processes, managing inventory, and optimising supply chain activities.
Management Information Systems are essential for modern organisations, providing critical support for decision-making, strategic planning, and operational control. By integrating and processing data from various sources, MIS delivers comprehensive insights that help managers optimise performance and achieve organisational goals. The ability to generate detailed and timely reports ensures that all levels of management have the information they need to make informed decisions.
Decision Support Systems (DSS):
These systems assist managers in making semi-structured or unstructured decisions by providing analytical tools and models. They are a crucial type of information system within the broader context of Management Information Systems (MIS). They are designed to assist managers and business professionals in making informed and data-driven decisions. DSS leverage data, sophisticated analytical models, and user-friendly interfaces to support decision-making processes in various organisational contexts.
Key Characteristics:
- Interactive Interface: DSS provide an interactive interface that allows users to engage with the system, inputting data, querying information, and generating reports.
- Analytical Tools: These systems incorporate analytical tools such as statistical analysis, optimization models, and simulation to analyse data and generate insights.
- Flexibility and Adaptability: DSS are designed to be flexible, allowing users to adapt the system to specific needs, scenarios, and decision-making contexts.
- Integration of Data: They integrate data from multiple sources, including internal databases, external data feeds, and historical records.
- User-Friendly Reports and Visualisations: DSS generate reports and visualisations that are easy to understand and interpret, aiding in the quick comprehension of complex data.
Functions of DSS:
- Data Management: DSS manage and store large volumes of data, ensuring it is accessible and organized for analysis.
- Model Management: They incorporate various analytical models that can be used to simulate scenarios, optimise outcomes, and analyse trends.
- Knowledge Management: DSS often include knowledge management components that help in storing and retrieving organisational knowledge and expertise.
- User Interface: The interface allows users to interact with the system, enter queries, and receive results in a user-friendly format.
Types of DSS:
- Data-Driven DSS: Focuses on the manipulation and analysis of large data sets. These systems are often used for business intelligence and analytics.
- Model-Driven DSS: Emphasises the use of mathematical models to simulate different scenarios and analyse the potential outcomes of various decisions.
- Knowledge-Driven DSS: Utilises expert systems and artificial intelligence to provide recommendations based on knowledge bases and rule sets.
- Communication-Driven DSS: Designed to facilitate communication and collaboration among team members, often used in group decision-making processes.
- Document-Driven DSS: Focuses on the management, retrieval, and manipulation of unstructured data in documents.
Benefits of DSS:
- Improved Decision Quality: By providing accurate and relevant data, DSS improve the quality of decisions made by managers and professionals.
- Enhanced Efficiency: Automating data analysis and reporting processes saves time and resources, allowing for quicker decision-making.
- Better Risk Management: DSS help in identifying and analysing potential risks, enabling proactive risk management strategies.
- Increased Flexibility: These systems allow organisations to quickly adapt to changing conditions and make informed decisions in real-time.
- Support for Complex Decisions: DSS are particularly valuable for complex and non-routine decisions that require in-depth analysis and consideration of multiple factors.
Examples of DSS Applications:
- Financial Planning: DSS are used to analyze financial data, create budgets, and forecast financial performance.
- Supply Chain Management: They help in optimizing supply chain operations, managing inventory, and forecasting demand.
- Healthcare Management: DSS assist in diagnosing medical conditions, planning treatment protocols, and managing patient data.
- Marketing Analysis: These systems are used to analyse market trends, segment customers, and develop marketing strategies.
- Human Resources Management: DSS support workforce planning, performance evaluation, and employee training programs.
Integration with Other Information Systems:
- Transaction Processing Systems (TPS): TPS provide the raw transactional data that DSS analyse to generate insights.
- Executive Information Systems (EIS): DSS feed into EIS by providing detailed analyses that help executives make strategic decisions.
- Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP): Data from ERP systems can be utilised by DSS to enhance decision-making across various business functions.
- Customer Relationship Management (CRM): DSS use data from CRM systems to analyze customer behavior and improve customer relationship strategies.
Decision Support Systems are an integral part of modern Management Information Systems, providing essential tools and capabilities for data-driven decision-making. By integrating data management, analytical models, and user-friendly interfaces, DSS enable organisations to make informed, efficient, and effective decisions. Their flexibility, adaptability, and ability to handle complex scenarios make them invaluable in various business contexts, from financial planning to supply chain management and beyond.
Executive Information Systems (EIS):
These systems provide critical information tailored for top-level executives to support strategic decision-making. They are specialised information systems designed to support senior management in decision-making processes. These systems provide executives with easy access to internal and external information that is relevant to their strategic goals and objectives. EIS are characterised by their ability to present data in a consolidated and summarised format, making it easier for executives to identify trends, patterns, and critical issues.
Key Characteristics:
- User-Friendly Interface: EIS are designed with a highly intuitive and interactive user interface, allowing executives to easily navigate and retrieve information without requiring extensive technical skills.
- Summarised Information: They focus on providing summarised and high-level information through dashboards, charts, and graphs, helping executives quickly grasp key insights.
- Real-Time Data Access: EIS offer real-time access to data, ensuring that executives are working with the most up-to-date information available.
- Customisable Reports: Users can customise reports to focus on specific metrics, key performance indicators (KPIs), and other relevant data points.
- Drill-Down Capabilities: While EIS present high-level summaries, they also offer the ability to drill down into more detailed data when needed.
- Integration with Other Systems: EIS integrate data from various internal and external sources, providing a comprehensive view of the business environment.
Functions of EIS:
- Performance Monitoring: EIS help executives monitor the performance of various business units and processes against predefined goals and benchmarks.
- Strategic Planning: By providing insights into market trends, competitive landscape, and internal performance, EIS assist in strategic planning and long-term decision-making.
- Risk Management: EIS enable the identification and assessment of potential risks, supporting proactive risk management strategies.
- Resource Allocation: They provide data that helps in making informed decisions about resource allocation, ensuring optimal use of financial, human, and physical resources.
- Trend Analysis: EIS facilitate the analysis of historical and current data to identify trends and forecast future scenarios.
Benefits of EIS:
- Enhanced Decision-Making: By providing relevant and timely information, EIS enhance the quality of decisions made by executives.
- Improved Efficiency: EIS streamline the process of data retrieval and analysis, saving time and resources.
- Greater Agility: With real-time data access, executives can respond more quickly to changes in the business environment.
- Better Strategic Alignment: EIS ensure that decisions are aligned with the strategic goals and objectives of the organisation.
- Increased Transparency: EIS promote transparency by providing clear and concise information on business performance and strategic initiatives.
Examples of EIS Applications:
- Financial Performance Analysis: EIS provide insights into financial metrics such as revenue, expenses, profit margins, and cash flow, helping executives manage financial performance.
- Market Analysis: They offer data on market trends, customer preferences, and competitor activities, supporting market analysis and strategy development.
- Operational Efficiency: EIS help monitor and improve operational efficiency by tracking key operational metrics and identifying areas for improvement.
- Human Resources Management: These systems provide information on workforce performance, talent management, and employee satisfaction, aiding in human resources management.
- Compliance and Governance: EIS ensure compliance with regulatory requirements by providing data on compliance metrics and governance standards.
Integration with Other Information Systems:
- Transaction Processing Systems (TPS): EIS use data from TPS to generate high-level summaries and reports.
- Management Information Systems (MIS): EIS are often considered an extension of MIS, providing more focused and high-level information for executives.
- Decision Support Systems (DSS): EIS may incorporate features of DSS to provide deeper analysis and support complex decision-making processes.
- Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP): Data from ERP systems is utilised by EIS to provide a holistic view of the organisation’s performance.
- Customer Relationship Management (CRM): EIS integrate CRM data to provide insights into customer behaviour, satisfaction, and sales performance.
Executive Information Systems (EIS) are essential tools within the broader framework of Management Information Systems (MIS). They provide executives with the necessary information to make strategic, data-driven decisions. By consolidating and summarising data from various sources, offering real-time insights, and supporting strategic planning, EIS play a crucial role in enhancing organisational performance and achieving strategic goals. Their integration with other information systems ensures a comprehensive and cohesive approach to business management and decision-making.
Benefits of an MIS:
Improved decision-making:
By providing accurate and timely information, an MIS can help managers make better-informed decisions. Here’s an in-depth look at how MIS enhances decision-making processes within organisations:
1. Access to Real-Time Data:
- Timely Information: MIS provides access to real-time data, which is crucial for making informed decisions. Managers can react to changes in the market, internal operations, or external factors swiftly.
- Data Accuracy: With real-time data, the accuracy of the information is significantly improved, reducing the risk of decisions based on out-dated or incorrect data.
2. Data Integration and Centralisation:
- Consolidated Information: MIS integrates data from various departments (e.g., finance, operations, marketing, etc) into a centralised system, providing a holistic view of the organisation’s performance.
- Elimination of Data Silos: By centralising data, MIS eliminates data silos, ensuring that all departments have access to the same information. This promotes consistency in decision-making across the organization.
3. Enhanced Analytical Capabilities:
- Data Analysis and Reporting: MIS includes tools for data analysis, which can identify trends, patterns, and anomalies. Advanced reporting capabilities help managers understand complex data through visualisations like charts and graphs.
- Predictive Analytics: Some MIS incorporate predictive analytics, enabling managers to forecast future trends and outcomes based on historical data. This helps in proactive decision-making rather than reactive.
4. Support for Strategic Planning:
- Long-Term Planning: MIS supports strategic planning by providing data that is essential for setting long-term goals and objectives. This includes market analysis, competitive analysis, and internal performance metrics.
- Scenario Analysis: Managers can use MIS to conduct scenario analysis, evaluating the potential impact of different strategies and decisions under various conditions. This aids in selecting the most viable strategy.
5. Improved Efficiency and Productivity:
- Streamlined Processes: MIS streamlines business processes by automating data collection, processing, and reporting. This reduces the time and effort required to gather and analyse information, allowing managers to focus on decision-making.
- Resource Allocation: With accurate and comprehensive data, managers can make better decisions about resource allocation, ensuring optimal use of financial, human, and physical resources.
6. Enhanced Communication and Collaboration:
- Information Sharing: MIS facilitates better communication and collaboration among departments by providing a unified platform for sharing information. This ensures that all stakeholders are informed and can contribute to the decision-making process.
- Transparency: Increased transparency in data and reporting enhances trust among team members and stakeholders, leading to more collaborative and effective decision-making.
7. Risk Management:
- Identifying Risks: MIS helps in identifying potential risks by analysing data and spotting trends that may indicate future problems. This allows managers to take preventive measures.
- Mitigating Risks: By providing detailed insights into various aspects of the business, MIS aids in developing risk mitigation strategies, ensuring that the organisation is prepared for potential challenges.
8. Enhanced Customer Insights:
- Understanding Customer Behaviour: MIS enables businesses to analyse customer data, gaining insights into customer preferences, behaviours, and feedback. This information is vital for making decisions that enhance customer satisfaction and loyalty.
- Personalised Marketing: With detailed customer insights, businesses can make data-driven decisions to personalise marketing efforts, improving engagement and conversion rates.
Management Information Systems (MIS) play a pivotal role in enhancing decision-making within organisations. By providing access to real-time data, integrating and centralising information, enhancing analytical capabilities, supporting strategic planning, improving efficiency, fostering communication, managing risks, and offering customer insights, MIS empowers managers to make more informed, effective, and strategic decisions. This ultimately leads to better organisational performance and a competitive edge in the market.
Increased efficiency:
Automating routine tasks and streamlining processes can improve operational efficiency and productivity. Here’s an in-depth discussion of how MIS contributes to increased efficiency:
1. Automation of Routine Tasks:
- Reduction in Manual Work: MIS automates repetitive and time-consuming tasks such as data entry, processing, and reporting. This reduces the need for manual intervention, thereby saving time and reducing the risk of human error.
- Streamlined Operations: By automating routine tasks, MIS enables employees to focus on more strategic and value-added activities, enhancing overall productivity.
2. Improved Data Management:
- Centralised Data Storage: MIS centralises data storage, ensuring that all information is stored in a single, accessible location. This eliminates the need for maintaining multiple, disparate data sources and simplifies data retrieval.
- Data Consistency and Accuracy: Centralised data management ensures that everyone in the organisation has access to consistent and accurate information, reducing the time spent verifying and reconciling data from different sources.
3. Enhanced Communication and Collaboration:
- Information Sharing: MIS provides platforms for information sharing across departments, facilitating better communication and collaboration. This ensures that all team members are on the same page and can work together more effectively.
- Reduced Information Silos: By integrating data from various departments, MIS reduces information silos, promoting a more collaborative and cohesive working environment.
4. Efficient Resource Allocation:
- Optimised Resource Use: MIS helps in tracking and analysing resource usage, enabling managers to allocate resources more effectively. This ensures that resources are used optimally and reduces wastage.
- Inventory Management: For businesses with significant inventory, MIS provides tools for inventory management, helping to maintain optimal inventory levels and reduce holding costs.
5. Improved Decision-Making Processes:
- Real-Time Data Access: MIS provides real-time access to data, which is critical for making timely and informed decisions. Managers can quickly analyse data and respond to changes in the business environment
- Advanced Reporting and Analytics: With robust reporting and analytics capabilities, MIS helps managers to gain insights into business performance and identify areas for improvement, leading to more efficient decision-making processes.
6. Enhanced Customer Service:
- Customer Relationship Management (CRM): MIS often includes CRM functionalities that help in managing customer interactions and data. This leads to better customer service by ensuring that customer inquiries and issues are handled efficiently.
- Personalised Services: By analysing customer data, MIS enables businesses to offer personalised services and recommendations, improving customer satisfaction and loyalty.
7. Operational Efficiency:
- Process Optimisation: MIS helps in identifying bottlenecks and inefficiencies in business processes. By analysing operational data, businesses can streamline processes and improve workflow efficiency.
- Performance Monitoring: Continuous monitoring of performance metrics through MIS allows for proactive management of operations, ensuring that any issues are addressed promptly and efficiently.
8. Cost Reduction:
- Lower Operational Costs: Automation and improved resource allocation lead to significant cost savings. Reduced manual work, optimised inventory levels, and efficient processes all contribute to lowering operational costs.
- Better Financial Management: MIS provides detailed financial reports and analytics, helping businesses to manage their finances better, control costs, and increase profitability.
Management Information Systems (MIS) significantly enhance the efficiency of organisations by automating routine tasks, improving data management, facilitating communication and collaboration, optimising resource allocation, supporting better decision-making, enhancing customer service, improving operational efficiency, and reducing costs. By leveraging MIS, organisations can achieve their objectives more effectively and maintain a competitive edge in their respective industries.
Better planning and control:
An MIS can support planning and forecasting activities, as well as monitor and control business operations. Here’s an in-depth discussion of how MIS contributes to these areas:
1. Enhanced Data Collection and Analysis:
- Comprehensive Data Access: MIS collects data from various departments and consolidates it into a centralised system. This comprehensive data access allows managers to have a holistic view of the organisation, which is vital for effective planning and control.
- Advanced Analytics: MIS provides advanced analytical tools that enable managers to process and analyse large volumes of data. These tools can identify trends, forecast future outcomes, and support strategic planning.
- Informed Decision-Making: By providing accurate and timely information, MIS helps managers make well-informed decisions. This reduces uncertainty and improves the quality of both strategic and operational plans.
2. Strategic Planning:
- Goal Setting and Alignment: MIS helps in setting organisational goals and aligning them with departmental and individual objectives. This alignment ensures that all parts of the organisation are working towards common goals.
- Scenario Analysis: Managers can use MIS to perform scenario analysis and evaluate the potential impact of different strategies. This helps in choosing the best course of action and preparing for possible future events.
- Resource Allocation: Efficient planning requires optimal resource allocation. MIS provides insights into resource availability and needs, enabling managers to allocate resources more effectively and avoid bottlenecks.
3. Operational Control:
- Monitoring Performance: MIS provides real-time monitoring of organisational performance against set benchmarks and goals. Managers can track key performance indicators (KPIs) and ensure that operations are running smoothly.
- Variance Analysis: By comparing actual performance with planned performance, MIS helps in identifying variances and their causes. This allows managers to take corrective actions promptly.
- Process Optimisation: MIS helps in identifying inefficiencies in processes and workflows. By analysing operational data, managers can implement improvements to enhance productivity and reduce waste.
4. Financial Control:
- Budgeting and Forecasting: MIS supports the budgeting process by providing accurate financial data and forecasts. This helps in creating realistic budgets and financial plans.
- Cost Control: Detailed financial reports generated by MIS allow for better cost control. Managers can monitor expenditures, identify areas of overspending, and implement cost-saving measures.
- Profitability Analysis: MIS provides insights into the profitability of different products, services, or business units. This helps in making informed decisions about pricing, investment, and resource allocation.
5. Inventory and Supply Chain Management:
- Inventory Optimisation: MIS helps in maintaining optimal inventory levels by providing real-time data on inventory status. This ensures that there is neither excess inventory nor stockouts, reducing carrying costs and improving customer satisfaction.
- Supply Chain Coordination: Effective supply chain management requires coordination between various stakeholders. MIS facilitates better communication and information sharing across the supply chain, enhancing coordination and efficiency.
6. Human Resource Management:
- Workforce Planning: MIS provides tools for workforce planning, including employee scheduling, skills assessment, and workload analysis. This ensures that the organisation has the right number of employees with the right skills at the right time.
- Performance Appraisal: MIS supports the performance appraisal process by providing accurate and objective data on employee performance. This helps in identifying high performers, addressing performance issues, and planning for employee development.
7. Risk Management:
- Identifying Risks: MIS helps in identifying potential risks by analysing data from various sources. This proactive approach allows managers to anticipate risks and develop mitigation strategies.
- Compliance and Reporting: MIS ensures compliance with regulatory requirements by providing accurate and timely reports. This reduces the risk of non-compliance and the associated penalties.
Management Information Systems (MIS) significantly enhance planning and control within organisations by providing accurate data, advanced analytics, real-time monitoring, and comprehensive reporting. These capabilities support strategic and operational planning, optimise resource allocation, improve financial management, streamline inventory and supply chain management, enhance human resource management, and strengthen risk management. By leveraging MIS, organisations can achieve their goals more effectively, maintain competitive advantage, and ensure long-term sustainability.
Competitive advantage:
By leveraging the power of information, organisations can gain a competitive edge in their respective industries. Here’s an in-depth discussion on how MIS contributes to competitive advantage:
1. Enhanced Decision-Making:
- Data-Driven Insights: MIS provides accurate and timely information, enabling managers to make informed decisions. This reduces the reliance on intuition and guesswork, leading to more effective strategies and operations.
- Real-Time Analytics: With real-time data analytics, managers can quickly respond to market changes and emerging opportunities. This agility is crucial for staying ahead of competitors.
2. Operational Efficiency:
- Streamlined Processes: MIS automates and optimises business processes, reducing manual work and errors. This leads to faster turnaround times and increased productivity.
- Resource Optimisation: By providing insights into resource usage and requirements, MIS helps in optimising the allocation of resources. This reduces waste and ensures that resources are used where they are most effective.
3. Customer Relationship Management (CRM):
- Enhanced Customer Insights: MIS integrates CRM systems that gather and analyse customer data. This allows businesses to understand customer preferences and behaviours, leading to better customer service and personalised marketing.
- Improved Customer Retention: By using MIS to enhance customer interactions and satisfaction, businesses can improve customer loyalty and retention, which are critical for long-term success.
4. Innovation and Product Development:
- Market Analysis: MIS provides tools for market analysis, helping businesses identify trends and customer needs. This information is vital for developing new products and services that meet market demands.
- Faster Time-to-Market: By streamlining product development processes and providing project management tools, MIS can help reduce the time it takes to bring new products to market, giving businesses a competitive edge.
5. Strategic Planning:
- Scenario Planning: MIS supports scenario planning and what-if analysis, enabling organisations to evaluate different strategic options and prepare for future contingencies.
- Performance Monitoring: With MIS, organisations can continuously monitor performance against strategic goals and make necessary adjustments. This ensures that the organisation stays on track to achieve its objectives.
6. Supply Chain Management:
- Enhanced Coordination: MIS improves coordination across the supply chain by providing real-time visibility into inventory levels, order status, and supplier performance. This leads to a more efficient and responsive supply chain.
- Cost Reduction: By optimising inventory levels and reducing lead times, MIS helps in lowering supply chain costs, which can be a significant competitive advantage.
7. Compliance and Risk Management:
- Regulatory Compliance: MIS helps in ensuring compliance with industry regulations by providing accurate and timely reports. This reduces the risk of legal penalties and enhances the organisation’s reputation.
- Risk Mitigation: By identifying potential risks through data analysis, MIS enables proactive risk management. This helps in mitigating risks before they impact the business.
8. Global Reach and Scalability:
- Market Expansion: MIS supports global operations by providing tools that enable businesses to manage and coordinate activities across different geographies. This facilitates market expansion and globalisation.
- Scalability: As businesses grow, MIS can scale to handle increased data volumes and complexity. This ensures that the organisation’s information systems can support its growth without compromising performance.
Management Information Systems (MIS) provide a wide range of benefits that collectively contribute to gaining and sustaining a competitive advantage. By enhancing decision-making, operational efficiency, customer relationship management, innovation, strategic planning, supply chain management, compliance, and global reach, MIS equips organisations with the tools and insights needed to outperform competitors and achieve long-term success.
Effective management information systems are critical for organisations to manage their operations, make informed decisions, and achieve their strategic goals in today's data-driven business environment.
Same Category
General Category
- Artificial General Intelligence (AGI) 8
- Robotics 5
- Algorithms & Data Structures 4
- Tech Business World 4
Sign Up to New Blog Post Alert